Ammonium Nitrate Fertilizer: How To Use Ammonium Nitrate In Gardens
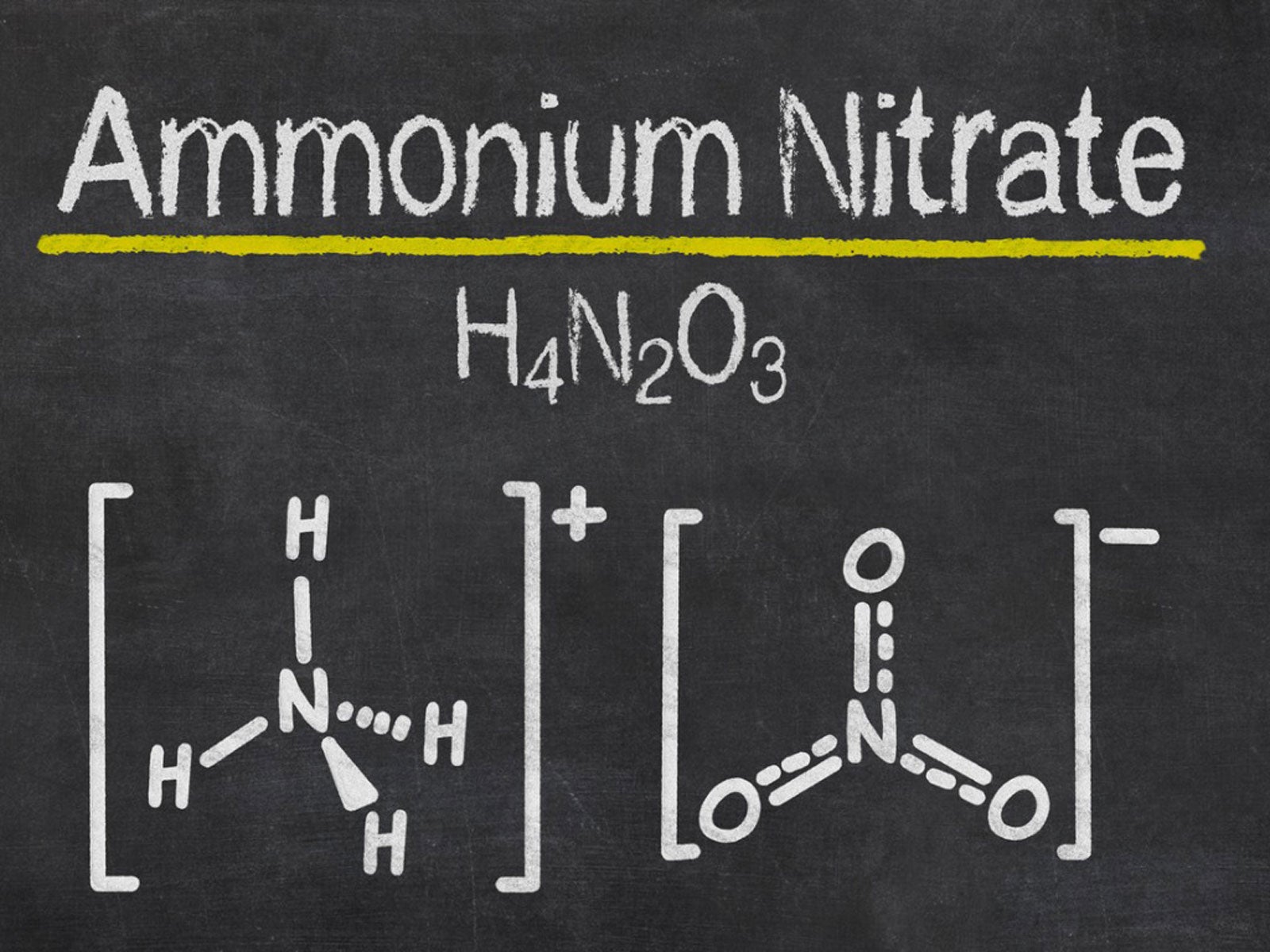

One of the key needs for successful plant growth is nitrogen. This macro-nutrient is responsible for the leafy, green production of a plant and enhances overall health. Nitrogen is derived from the atmosphere, but this form has a strong chemical bond that is difficult for plants to uptake. Easier forms of nitrogen that occur in processed fertilizers include ammonium nitrate. What is ammonium nitrate? This type of fertilizer has been widely used since the 1940's. It is a fairly simple compound to make and is inexpensive, making it a top choice for agricultural professionals.
What is Ammonium Nitrate?
Nitrogen comes in many forms. This major plant nutrient can be taken in by plants through the roots or from the stoma in the leaves and stems. Additional sources of nitrogen are often added to soil and plants in areas without sufficient natural sources of nitrogen. One of the first solid nitrogen sources produced in a large scale capacity is ammonium nitrate. Ammonium nitrate fertilizer is the most common use of the compound, but it also has a very volatile nature, which makes it useful in certain industries. Ammonium nitrate is an odorless, nearly colorless crystal salt. Using ammonium nitrate in gardens and large-scale agricultural fields enhances plant growth and provides a ready supply of nitrogen from which plants can draw. Ammonium nitrate fertilizer is a simple compound to make. It is created when ammonia gas reacts with nitric acid. The chemical reaction produces a concentrated form of ammonium nitrate, which produces prodigious amounts of heat. As a fertilizer, the compound is applied as granules and fused with ammonium sulfate to minimize the volatile nature of the compound. Anti-caking agents are also added to the fertilizer.
Other Uses for Ammonium Nitrate
In addition to its usefulness as a fertilizer, ammonium nitrate is also employed in certain industrial and construction settings. The chemical compound is explosive and useful in mining, demolition activities, and quarry work. The granules are very porous and can absorb large amounts of fuel. Exposure to fire will cause a long, sustained, and large explosion. In most cases, the compound is very stable and can only become explosive in certain conditions. Food preservation is another area that is using ammonium nitrate. The compound makes an excellent cold pack when one bag of water and one bag of the compound are united. Temperatures can drop to 2 or 3 degrees Celsius very rapidly.
How to Use Ammonium Nitrate
Ammonium nitrate in gardens is made stable with other compounds. The fertilizer is an almost instantly useable form of nitrogen due to its porosity and solubility. It provides nitrogen from both ammonia and nitrate. The standard method of application is by broadcast spreading the granules. These will rapidly melt in water to allow the nitrogen to release into the soil. The rate of application is 2/3 to 1 1/3 cup (157.5 - 315 ml.) of ammonium nitrate fertilizer per 1,000 square feet (93 sq. m.) of land. After broadcasting the compound, it should be tilled in or watered in very thoroughly. The nitrogen will move quickly through the soil to the roots of the plant for rapid uptake. The most common uses for the fertilizer are in vegetable gardens and in hay and pasture fertilization due to the high nitrogen content.
Gardening tips, videos, info and more delivered right to your inbox!
Sign up for the Gardening Know How newsletter today and receive a free copy of our e-book "How to Grow Delicious Tomatoes".

Bonnie Grant is a professional landscaper with a Certification in Urban Gardening. She has been gardening and writing for 15 years. A former professional chef, she has a passion for edible landscaping.